Forging Parts
What is forging ?
Forging refers to the process of shaping metal (or other materials) by heating it to a high temperature and then hammering or pressing it into the desired shape. The process of forging is typically used to create strong and durable objects, such as tools, weapons, and machine parts. The metal is heated until it becomes soft and malleable, and then it is placed on an anvil and shaped using a hammer or press.
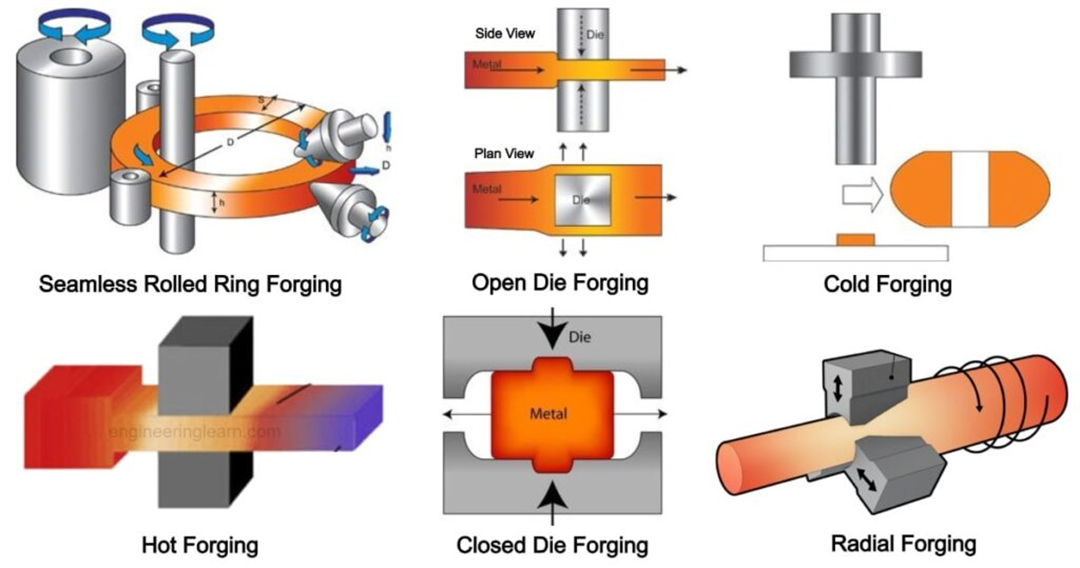
Forging Types
Forging is a metal forming process in which a metal material is heated to a plastic state and force is applied to deform it into the desired shape. According to different classification methods, forging can be divided into different types, the following are some common classification methods:
- According to the different forging materials, forging can be divided into the following types:
Brass forging: refers to various forging processes on brass and its alloys.
Aluminum alloy forging: refers to various forging processes for aluminum and its alloys.
Titanium alloy forging: refers to various forging processes for titanium and its alloys.
Stainless steel forging: refers to various forging processes for stainless steel and its alloys.
- According to the different forging shapes, forging can be divided into the following types:
Flat forging: pressing metal materials into a flat shape according to a certain thickness and width.
Cone Forging: Pressing a metal material into a conical shape.
Bending forging: forming the metal material into the desired shape by bending.
Ring forging: Forging a metal material into a ring shape.
- According to the different forging pressure, forging can be divided into the following types:
Stamping: The working of metal under low pressure, usually suitable for the production of thinner metal parts.
Medium-pressure forging: Requires greater pressure than stamping and is usually suitable for producing parts of medium thickness.
High Pressure Forging: Forging requires a lot of pressure and is usually suitable for producing thicker parts.
- According to different forging applications, forging can be divided into the following types:
Auto parts forging: Manufacture various parts that need to be used in cars, such as engine parts, chassis parts, etc.
Aerospace forging: parts required for manufacturing aircraft, rockets and other aerospace devices.
Energy Forging: Manufacture parts needed in various energy equipment, such as boilers, gas turbines, etc.
Mechanical forging: Manufacture parts that need to be used in various mechanical equipment, such as bearings, gears, connecting rods, etc.